Medicare
Medicare is the federal government healthcare program that subsidizes healthcare services for adults over 65. The plan also covers people younger than 65 who qualify through disability and those with certain diseases, including end-stage renal disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease). To qualify for Medicare, an individual must be either a U.S. citizen or a legal permanent resident that has been in the country for at least five continuous years.
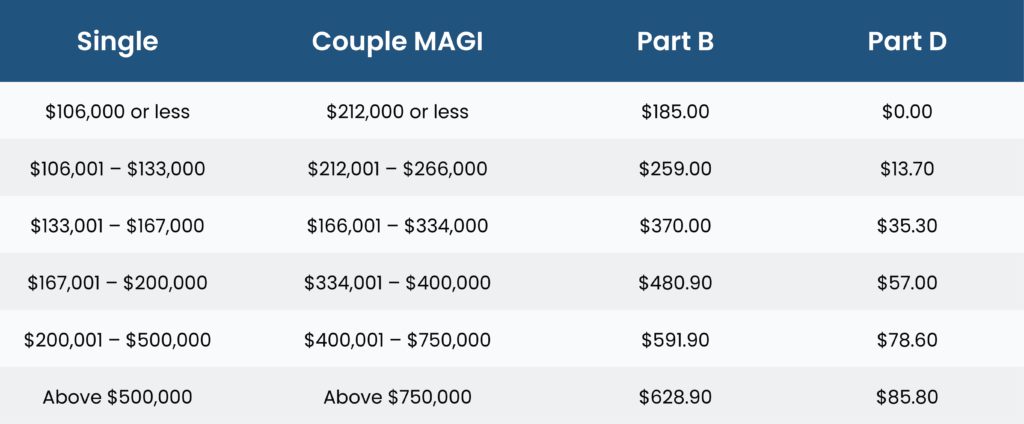
Medicare is separated into different parts that cover a variety of medical situations. While Medicare provides beneficiaries with more choices in terms of coverage and costs, it also presents complexity for the people looking to enroll. Here is an overview of how Medicare parts.